Previous Next
Array
An array is a lineardata structure consisting of a collection of similar data type elements, eachidentified by at least one index or key. The size of the array must bespecified at the time of its declaration. It is fixed and cannot be resizedduring runtime. In the array, elements are organized sequentially, one after anotherwithin a single block of memory.
- Access – It supports efficient random access,which means that its elements can be accessed directly using their index.
- Insertion – If the insertion site is located atthe beginning or in the middle of the array, all the elements located on theright are moved one index forward. If the array is full, a new larger array iscreated. Inserting is very efficient at the end of the array.
- Deletion – If the deleted element is located atthe beginning or in the middle of the array, all the elements located on the leftare moved one index backwards to avoid leaving an empty space in memory. Thisguarantees that the elements are stored in contiguous space in memory. Removal isvery efficient at the end of the array because only the last element is deleted.
- Search – The array must be sequentially checkeduntil a match is found.

Linked List
A linked list is a lineardata structure consisting of nodes (elements) where each node contains a datafield and a reference (link) to the next node in the list. Extra memory spacefor a pointer is required with each element of the list. The first node iscalled the head. The last node iscalled the tail. The size of the linkedlist doesn’t need to be specified at the time of its declaration. It allows dynamicresizing at runtime. There is no requirement for the list’s elements to bestored contiguously in memory because pointers are used to link the data.
- Access – Random access is not allowed. Elements mustbe accessed sequentially starting from the first node.
- Insertion – It could be implemented efficientlyif the element is inserted at the head (first node) because there is no relinkingof nodes to be performed since the first node has no preceding node. Insertinga node at the middle requires the preceding node to refer to the node we wantto add. Inserting a node at the end (tail) requires the preceding node to referto the new end of the list.
- Deletion – It could be implemented efficientlyif the element is removed from the head (first node) because there is no relinkingof nodes to be performed since the first node has no preceding node. Removing anode from the middle requires preceding node to refer to the node before theone we want to remove. Removing a node from the end (tail) requires thepreceding node to become the new end of the list (i.e., points to nothing afterit).
- Search – The linked list must be sequentially checkeduntil a match is found.
Hash Table
A hash table is an unorderedcollection of elements consisting of key-value pairs. A hash table isimplemented using a hashing function. It improves data access times. Ratherthan sorting the data according to a key, it computes the location of the datafrom the key. In simple terms, it computes an index value from the key of thedesired record. At that index value, the record is stored/retrieved.
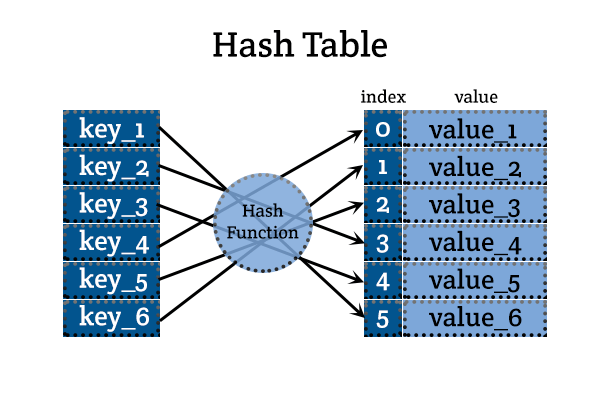
A good hash function is essential for hash tableperformance. A poor choice of hash function is likely to lead to an excess amountof collisions which will degrade performance significantly. Also some hashfunctions are computationally expensive and the amount of time (and, in somecases, memory) taken to compute the hash may be burdensome. The primaryrequirements in implementing a good hash function for a given data type arethat it should be deterministic (equal keys must produce the same hash value),efficient to compute and to distribute the keys uniformly.
The complexity of a hash table depends on the hash function picked. The more collisions it generates, the more the complexity tends toward Θ(n). Hash tables have a Θ(1) complexity in best and average case scenarios but fall to Θ(n) in their worst-case scenario.
Data Structure | Time Complexity (Average) | Time Complexity (Worst) | Space Complexity | ||||||
Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion | Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion | ||
Array | Θ(1) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) |
Linked List | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | Θ(n) |
Hash Table | N/A | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | Θ(1) | N/A | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) | Θ(n) |
Conclusion
Arrays and linked lists are data structures which store acollection of elements in a specific order. In arrays, the order of elements isfixed and they’re accessed sequentially by index number. In linked lists, the nodescan be in any place in memory, because each of them has a pointer to the nextnode. A hash table is different from either because it doesn’t store its elementsin any particular order. It is an unordered collection of elements withdifferent (usually quick) access times, which in practice can be somewherebetween the array and the linked list based on how exactly it is implementedand used.
In short, if you have data that doesn’t use too many insertsor deletes, and access the items frequently out of order, use an array. If youneed data that can be quickly inserted and deleted into and is accessed mostlyin sequential order, use a linked list. If you need a fast traversal then a hashtable with a good hash function will be a better choice.
Was this article helpful?
If you have any suggestions or questions, please leave a comment below.
2019-06-10T22:24:21+03:00By Open4Tech Team|Categories: Explained Simply|Tags: data structures|0 Comments
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
FacebookXRedditLinkedInWhatsAppTumblrPinterestVkEmail
Related Posts

Bubble Sort Algorithm
Gallery
Bubble Sort Algorithm
August 10th, 2020|0 Comments
KiCad Files – Useful Information
KiCad Files – Useful Information
July 6th, 2020|0 Comments

IPv6 Header Explained
Gallery
IPv6 Header Explained
June 15th, 2020|0 Comments
IPv4 Header Explained
IPv4 Header Explained
May 11th, 2020|0 Comments
IPv4 vs. IPv6
IPv4 vs. IPv6
May 4th, 2020|1 Comment
Namespaces vs Modules in TypeScript
Namespaces vs Modules in TypeScript
March 2nd, 2020|0 Comments
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.