Last Updated : 27 Jun, 2024
Summarize
Comments
Improve
In cryptography, it is a very monotonous task to distribute the public and private keys between sender and receiver. If the key is known to the third party (forger/eavesdropper) then the whole security mechanism becomes worthless. So, there comes the need to secure the exchange of keys. In this article, we will learn about key management, how Cryptographic Keys Work, Types of Key Management, and Key Management Lifecycle.
What is Key Management?
Key management refers to the processes and procedures involved in generating, storing, distributing, and managing cryptographic keys used in cryptographic algorithms to protect sensitive data. It ensures that keys used to protect sensitive data are kept safe from unauthorized access or loss. Good key management helps maintain the security of encrypted information and is important for protecting digital assets from cyber threats. Effective key management is crucial for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of encrypted information by securing cryptographic keys from unauthorized access, loss, or compromise.
How Cryptographic Keys Works?
Cryptographic keys are special codes that protect information by locking (encrypting) and unlocking (decrypting) it. In symmetric key cryptography, a single shared key does both jobs, so the same key must be kept secret between users. In asymmetric key cryptography, there are two keys: a public key that anyone can use to encrypt messages or verify signatures, and a private key that only the owner uses to decrypt messages or create signatures. This makes it easier to share the public key openly while keeping the private key secret. These keys are crucial for secure communication, like when you visit a secure website (HTTPS), where they help encrypt your data and keep it safe from eavesdroppers and criminals. So, to manage these keys properly is vital to keep digital information secure and dependable.
Types of Key Management
There are two aspects of Key Management:
- Distribution of public keys.
- Use of public-key encryption to distribute secrets.
Distribution of Public Key
The public key can be distributed in four ways:
- Public announcement
- Publicly available directory
- Public-key authority
- Public-key certificates.
These are explained as following below:
1. Public Announcement:Here the public key is broadcast to everyone. The major weakness of this method is a forgery. Anyone can create a key claiming to be someone else and broadcast it. Until forgery is discovered can masquerade as claimed user.

2. Publicly Available Directory:In this type, the public key is stored in a public directory. Directories are trusted here, with properties like Participant Registration, access and allow to modify values at any time, contains entries like {name, public-key}.Directories can be accessed electronically still vulnerable to forgery or tampering.
3. Public Key Authority:It is similar to the directory but, improves security by tightening control over the distribution of keys from the directory. It requires users to know the public key for the directory. Whenever the keys are needed, real-time access to the directory is made by the user to obtain any desired public key securely.
4. Public Certification:This time authority provides a certificate (which binds an identity to the public key) to allow key exchange without real-time access to the public authority each time. The certificate is accompanied by some other info such as period of validity, rights of use, etc. All of this content is signed by the private key of the certificate authority and it can be verified by anyone possessing the authority’s public key.
First sender and receiver both request CA for a certificate which contains a public key and other information and then they can exchange these certificates and can start communication.
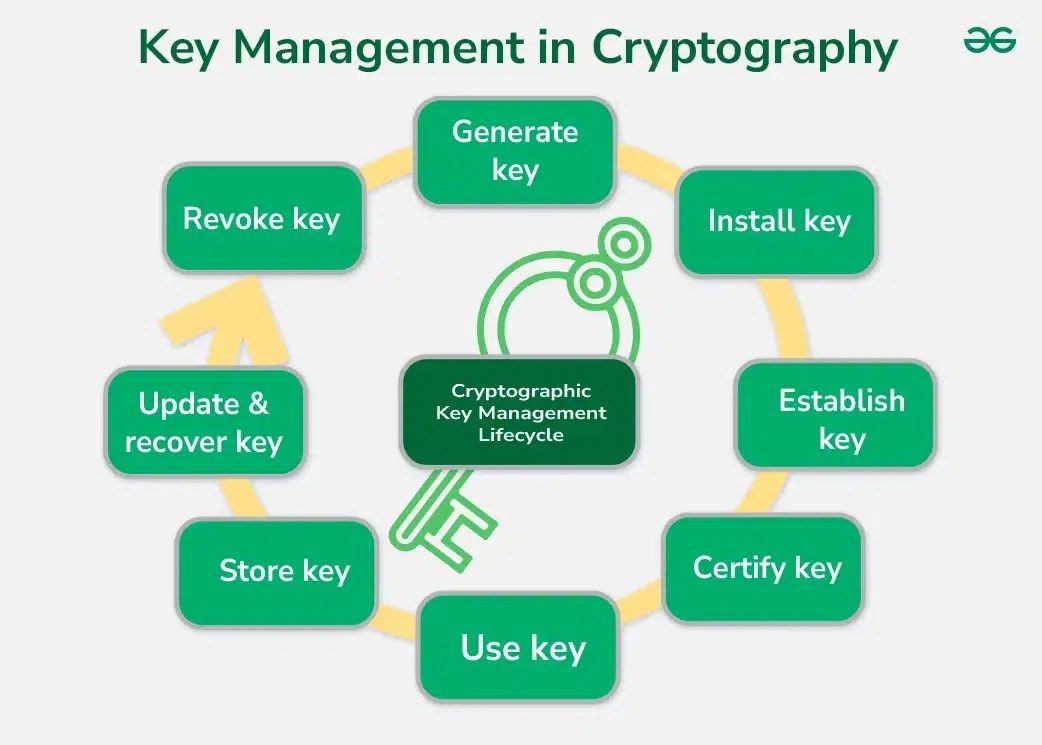
Key Management Lifecycle
The key management lifecycle outlines the stages through which cryptographic keys are generated, used, and eventually retired or destroyed. Proper management of these keys is critical to ensuring the security of cryptographic systems. Here’s an overview of each stage:
1. Key Generation:
- Creation: Keys are created using secure algorithms to ensure randomness and strength.
- Initialization: Keys are initialized with specific parameters required for their intended use (e.g., length, algorithm).
2. Key Distribution:
- Sharing: For symmetric keys, secure methods must be used to share the key between parties.
- Publication: For asymmetric keys, the public key is shared openly, while the private key remains confidential.
3. Key Storage:
- Protection: Keys must be stored securely, typically in hardware security modules (HSMs) or encrypted key stores, to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Only authorized users or systems should be able to access keys.
4. Key Usage:
- Application: Keys are used for their intended cryptographic functions, such as encrypting/decrypting data or signing/verifying messages.
- Monitoring: Usage is monitored to detect any unusual or unauthorized activities.
Key Management in Cryptography
5. Key Rotation:
- Updating: Keys are periodically updated to reduce the risk of exposure or compromise.
- Re-Keying: New keys are generated and distributed, replacing old ones while ensuring continuity of service.
6. Key Revocation:
- Invalidation: Keys that are no longer secure or needed are invalidated.
- Revocation Notices: For public keys, revocation certificates or notices are distributed to inform others that the key should no longer be trusted.
7. Key Archival:
- Storage: Old keys are securely archived for future reference or compliance purposes.
- Access Restrictions: Archived keys are kept in a secure location with restricted access.
8. Key Destruction:
- Erasure: When keys are no longer needed, they are securely destroyed to prevent any possibility of recovery.
- Verification: The destruction process is verified to ensure that no copies remain.
Conclusion
Managing cryptographic keys is crucial for keeping data secure. It involves creating, distributing, storing, using, updating, and eventually destroying keys properly. Good key management ensures that keys are safe from unauthorized access and can be trusted throughout their life. By doing this, organizations protect sensitive information and maintain the security of their digital communications. In short, effective key management is essential for making encryption work and keeping information systems secure.
Frequently Asked Questions on Key Management in Cryptography
What is the function of key management system?
The purpose of key management is to handle keys throughout their life from creation to storage, distribution, updating, control, and finally, destruction to keep them secure.
Why is key management important for security?
Key management is essential for data security. Encryption keys are used to lock and unlock data, so if a key is lost or compromised, data security is at risk. Keys also help in securely sending data over the Internet.
What is the goal of key management?
The main goal of key management is to protect sensitive data by securely handling cryptographic keys at every stage. This means ensuring keys are strong, shared safely, stored securely, updated regularly, and deleted properly when they are no longer needed.
Previous Article
Whirlpool Hash Function in Python
Next Article
Types of Authentication Protocols
