A class of ratios that measure the indebtedness of a firm
Written byCFI Team
Over 2 million + professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Unlock the essentials of corporate finance with our free resources and get an exclusive sneak peek at the first module of each course. Start Free
What are Leverage Ratios?
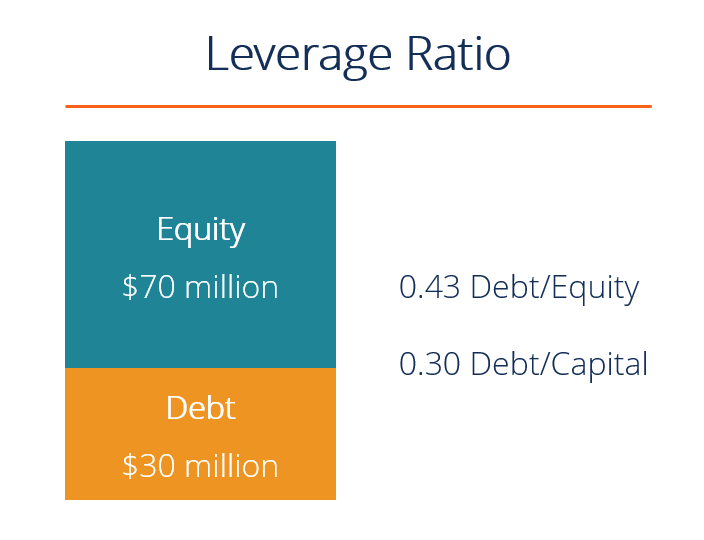
A leverage ratio is any kind of financial ratio that indicates the level of debt incurred by a business entity against several other accounts in its balance sheet, income statement, or cash flow statement. These ratios provide an indication of how the company’s assets and business operations are financed (using debt or equity). Below is an illustration of two common leverage ratios: debt/equity and debt/capital.
List of common leverage ratios
There are several different leverage ratios that may be considered by market analysts, investors, or lenders. Some accounts that are considered to have significant comparability to debt are total assets, total equity, operating expenses, and incomes.
Below are 5 of the most commonly used leverage ratios:
- Debt-to-Assets Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
- Debt-to-Capital Ratio = Total Debt / (Total Debt + Total Equity)
- Debt-to-EBITDA Ratio = Total Debt / Earnings Before Interest Taxes Depreciation & Amortization (EBITDA)
- Asset-to-Equity Ratio = Total Assets/ Total Equity
Leverage ratio example #1
Imagine a business with the following financial information:
- $50 million of assets
- $20 million of debt
- $25 million of equity
- $5 million of annual EBITDA
- $2 million of annual depreciation expense
Now calculate each of the 5 ratios outlined above as follows:
- Debt/Assets = $20 / $50 = 0.40x
- Debt/Equity = $20 / $25 = 0.80x
- Debt/Capital = $20 / ($20 + $25) = 0.44x
- Debt/EBITDA = $20 / $5 = 4.00x
- Asset/Equity = $50 / $25 = 2.00x

Download the Free Template
Enter your name and email in the form below and download the free template now!
Leverage ratio example #2
If a business has total assets worth $100 million, total debt of $45 million, and total equity of $55 million, then the proportionate amount of borrowed money against total assets is 0.45, or less than half of its total resources. When comparing debt to equity, the ratio for this firm is 0.82, meaning equity makes up a majority of the firm’s assets.
Importance and usage
Leverage ratios represent the extent to which a business is utilizing borrowed money. It also evaluates company solvency and capital structure. Having high leverage in a firm’s capital structure can be risky, but it also provides benefits.
The use of leverage is beneficial during times when the firm is earning profits, as they become amplified. On the other hand, a highly levered firm will have trouble if it experiences a decline in profitability and may be at a higher risk of default than an unlevered or less levered firm in the same situation.
Finally, analyzing the existing level of debt is an important factor that creditors consider when a firm wishes to apply for further borrowing.
Essentially, leverage adds risk but it also creates a reward if things go well.
What are the various types of leverage ratios?
1. Operating leverage
An operating leverage ratio refers to the percentage or ratio of fixed costs to variable costs. A company that has high operating leverage bears a large proportion of fixed costs in its operations and is a capital intensive firm. Small changes in sales volume would result in a large change in earnings and return on investment.
A negative scenario for this type of company could be when its high fixed costs are not covered by earnings because the market demand for the product decreases. An example of a capital-intensive business is an automobile manufacturing company.
If the ratio of fixed costs to revenue is high (i.e., >50%) the company has significant operating leverage. If the ratio of fixed costs to revenue is low (i.e., <20%) the company has little operating leverage.
2. Financial leverage
A financial leverage ratio refers to the amount of obligation or debt a company has been or will be using to finance its business operations. Using borrowed funds, instead of equity funds, can really improve the company’s return on equity and earnings per share, provided that the increase in earnings is greater than the interest paid on the loans. Excessive use of financing can lead to default and bankruptcy. See the most common financial leverage ratios outlined above.
3. Combined leverage
A combined leverage ratio refers to the combination of using operating leverage and financial leverage. For example, when viewing the balance sheet and income statement, operating leverage influences the upper half of the income statement through operating income while the lower half consists of financial leverage, wherein earnings per share to the stockholders can be assessed.
How is leverage created?
Leverage is created through various situations:
- A company takes on debt to purchase specific assets. This is referred to as “asset-backed lending” and is very common in real estate and purchases of fixed assets like property, plant, and equipment (PP&E).
- A company borrows money based on the overall creditworthiness of the business. This is usually a type of “cash flow loan” and is generally only available to larger companies.
- When a company borrows money to finance an acquisition (learn more about the mergers and acquisitions process).
- When a private equity firm (or other company) does a leveraged buyout (LBO).
- When an individual deals with options, futures, margins, or other financial instruments.
- When a person purchases a house and decides to borrow funds from a financial institution to cover a portion of the price. If the property is resold at a higher value, a gain is realized.
- Equity investors decide to borrow money to leverage their investment portfolio.
- A business increases its fixed costs to leverage its operations. Fixed costs do not change the capital structure of the business, but they do increase operating leverage which will disproportionately increase/decrease profits relative to revenues.
What are the risks of high operating leverage and high financial leverage?
If leverage can multiply earnings, it can also multiply risk. Having both high operating and financial leverage ratios can be very risky for a business. A high operating leverage ratio illustrates that a company is generating few sales, yet has high costs or margins that need to be covered. This may either result in a lower income target or insufficient operating income to cover other expenses and will result in negative earnings for the company.
On the other hand, high financial leverage ratios occur when the return on investment (ROI) does not exceed the interest paid on loans. This will significantly decrease the company’s profitability and earnings per share.
Coverage ratios
Besides the ratios mentioned above, we can also use the coverage ratios in conjunction with the leverage ratios tomeasure a company’s ability to pay itsfinancial obligations.
The most common coverage ratios are:
- Interest coverage ratio:The ability of a company to pay theinterest expense(only) on its debt
- Debt service coverage ratio: The ability of a company to pay all debt obligations, including repayment of principal and interest
- Cash coverage ratio:The ability of a company to pay interest expense with its cash balance
- Asset coverage ratio:The ability of a company to repay its debt obligations with its assets
Additional Resources
This leverage ratio guide has introduced the main ratios: Debt/Equity, Debt/Capital, Debt/EBITDA, etc. Below are additional relevant CFI resources to help you advance your career.